It is crucial to establish a robust corporate tax governance framework that fosters cooperative compliance and collaboration between taxpayers and tax authorities.
In brief
- Having a framework for tax governance improves compliance and creates a structured approach for businesses to prepare and adjust to constantly evolving tax laws and regulations.
- A well-developed and strong tax governance framework assists businesses in addressing gaps in the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) agenda.
- Implementing an appropriate tax governance framework can effectively manage tax-related risks, reduce long-term costs associated with compliance, and establish a transparent relationship between taxpayers and tax authorities.
In this era of tax transparency, having sound tax corporate governance is vital to any business operation. There is concerted focus and efforts by tax authorities around the world to reduce tax leakages through the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) and BEPS 2.0 initiatives; greater collaboration and exchange of information between tax authorities across jurisdictions; and the digitalisation of business and commerce transactions as well as tax authority functions. At the same time, many countries have taken the step to introduce tax corporate governance in the taxation system, to ensure that companies have established frameworks, systems and policies within their organisations that adhere to the prevailing tax rules and requirements.
In Malaysia, the Inland Revenue Board of (IRB) introduced the Tax Corporate Governance Framework (TCGF) on 11 April 2022 and subsequently the Guidelines on TCGF on 27 July 2022 to assist companies in designing and operating their tax governance frameworks and encourage them to voluntarily participate in the TCGF programme. The key objective of TCGF, which is regarded by IRB as “best practice” for taxpayers to adopt, is to build greater transparency in the tax affairs of companies. This in turn, will provide greater certainty for taxpayers in meeting their tax compliance obligations and help expedite the resolution of tax issues.
A taxpayer, whose TCGF has met IRB’s requirements and has received an authentication letter from IRB, will enjoy benefits such as reduced scrutiny (e.g., fewer tax audits), expedited tax refunds and the appointment of a dedicated IRB officer as a single point of contact in relation to the taxpayer’s tax matters. The TCGF programme is currently in its pilot phase until June 2024. Some corporates have received invitations to participate in the pilot TCGF programme, while others that are keen to participate can also reach out to IRB to be considered for the programme.
The TCGF programme is suitable for all types of businesses and provides the foundation in achieving good tax governance. It promotes co-operative compliance and a more collaborative relationship between taxpayers and the tax authority.
With improved tax governance, companies will be able to better manage tax and reputational risks, as well as mitigate the risk of penalties. The TCGF programme will also enable taxpayers and IRB to better manage and focus their resources.
Farah Rosley – Malaysia Tax Managing Partner
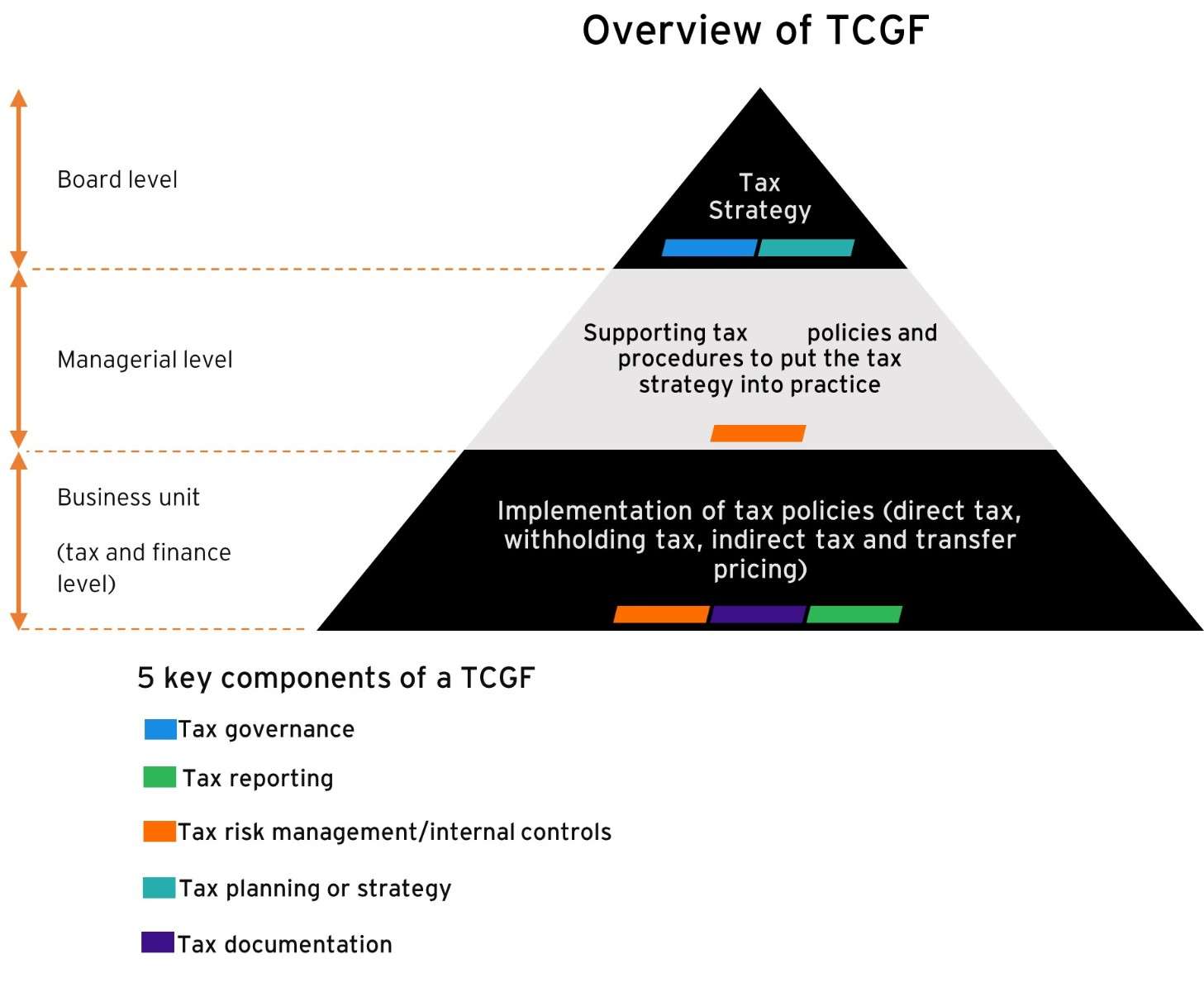
What Goes into a TCG Framework?
A framework of formally documented policies and operational procedures that:
- Identify tax risk
- Escalate tax risk
- Mitigate tax risk
Tax Corporate Governance Around the World
Countries such as Australia and Japan have a tax governance framework and guidance in place. The Australia Taxation Office (ATO) has established a tax governance benchmark through its Justified Trust Program. In this programme, the governance of a company is formally reviewed by the ATO. This places greater accountability on the board and management team in managing an organisation’s tax risks. In February 2022, the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) published its tax governance and tax risk management initiatives on its website, to promote the adoption of good tax governance principles and practices among large companies. Subsequently, in March 2022, IRAS introduced the Tax Governance Framework (TGF) and Tax Risk Management and Control Framework for Corporate Income Tax (CTRM) to strengthen tax compliance by large companies.
A good tax corporate governance will help companies:
- Enhance compliance with tax rules and regulations
- Address environmental, social and governance (ESG) considerations
- Demonstrate effective and sustainable tax risk management to stakeholders
- Have good internal controls to identify and manage tax risks early
- Establish an open, honest relationship with the tax authorities
- Reduce compliance costs in the long term
Enhance Compliance with Tax Rules and Regulations
The speed of change in the tax regulatory landscape continues to accelerate and so, keeping abreast with the latest changes can remain a challenge. Having a tax governance framework will help companies put in place a formalised structure to prepare for and adapt to the ever-changing tax rules and regulations, and enable them to readily apply the rules to business transactions as they happen.
Today’s digital age means that organisations need to transform their business models to stay relevant and competitive. Correspondingly, the regulatory environment is evolving, to get ahead of or keep up with the changes in the business landscape. There is pressure for businesses to stay abreast with these regulatory changes, to ensure that accurate and relevant data are being captured and the correct treatment is being adopted in computing and meeting their tax obligations.
Address Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Considerations
The ESG agenda is becoming a key priority in an organisation’s corporate strategy and a vital element in the board and senior management agenda.
Having good tax governance falls within the key ESG considerations for businesses. An established and robust tax governance framework helps businesses address gaps and be aware of actions required to rectify any potential issues, rather than taking a wait-and-see approach. It is also imperative that an organisation’s tax function evolves to ensure tax is always considered when formulating the ESG and sustainability strategies of the business.
Demonstrate Effective and Sustainable Tax Risk Management to Stakeholders
Managing stakeholders’ expectations is paramount and stakeholders expect companies to demonstrate effective tax governance measures focused on strategy and risk management. A tax governance framework helps companies to build in the right infrastructure that supports effective risk management and tax decision making, and ultimately, voluntary compliance. By ensuring the operational effectiveness of the tax governance framework and key internal controls, companies can address their disclosures on tax risk management, and at the same time, demonstrate the sustainability of their business from an ESG standpoint in their stakeholder communications. This will help enhance stakeholder comfort and confidence.
Have Good Internal Controls to Identify and Manage Tax Risks Early
Failure to manage tax risks can give rise to legal, financial and reputational risks. A tax governance framework helps companies identify and understand the key tax risks, including the potential focus areas by tax authorities. This will allow for a better management of tax risks upfront. At the same time, mitigation actions and improvements can be developed and implemented proactively as business transactions happen and as business structures are put in place, rather than during a tax audit.
The tax governance framework will also provide boards and senior management enhanced oversight of their tax risks and strategy. With a more comprehensive overview, boards and senior management teams can ask the right questions and obtain the relevant information to make key business decisions. This will further strengthen the controls and management of tax risks in transactions as they occur.
Establish an Open, Honest Relationship with the Tax Authorities
When engaging the tax authorities, having good internal tax governance will support effective interactions and provide clarity. It is important for the taxpayer and the tax authorities to work together in improving tax compliance, in an honest and transparent manner. This will result in a win-win outcome, where companies are able to meet their tax obligations and reduce the margin of error, and tax authorities are able to better focus their resources and enforcement efforts.
Reduce Compliance Costs in the Long Term
An effective tax governance framework can effectively reduce future tax compliance costs, in the form of greater process efficiencies, better certainty on tax positions, improved tax risk mitigation and reduced manpower time spent in compliance activities. This means that the time currently dedicated to compliance activities can be channelled to other value-adding business activities.
By integrating the necessary internal controls and strategic review mechanisms into the tax governance framework, companies will be able to better gauge the effectiveness of their tax risk management and avoid unnecessary tax costs in the long run.
In implementing the tax corporate governance framework, businesses will need to prioritise the following actions:
- Re-examine tax governance policy and control – to establish and include tax as part of the company’s corporate governance and risk management control
- Manage tax risks for future sustainability – expand the risk universe to include tax risks
- Articulate the contribution to the nation’s tax revenue collections and ensure a fair amount of taxes is paid
- Invest in tax skillsets and capabilities and achieve the right balance between internal and external resources – identify future-ready talent with tax skillsets that are capable of adapting to the changes of tax law and regulations. This includes developing a dynamic tax learning infrastructure
- Automate the tax function to ensure it is future-fit such as leveraging digital capabilities for tax risk management tasks (e.g., data collection, processing and reporting)
Conclusion
Tax corporate governance within the organization allows for better control of tax affairs and minimises the element of surprise and the risk of not identifying or anticipating the tax issues upfront.
The complex and ever-evolving business and regulatory environments, coupled with enhanced stakeholder scrutiny and expectations, reinforce the heightened focus on and importance of good tax governance for businesses. It is vital that businesses demonstrate to all stakeholders, visible and robust tax governance within their organisations, to minimise the financial, regulatory and reputational risks, today and beyond.
Summary
With the business environment changing and stakeholders expecting more transparency, strong tax governance is increasingly important for minimizing risks and maintaining a good reputation. It is crucial for businesses to implement visible and reliable tax governance measures to minimize financial, regulatory, and reputational risks.

 5.0
5.0