This is the first part of a three part series article.
- Second article | Top 5 (Generative) AI Risks for Businesses and How to Address Them Successfully
- Third article | Embracing (Generative) AI As A Strategic Advantage
Is it taking over jobs or revolutionising the way we do business and live?

Technology is forever evolving, and it can be a real struggle trying to keep up with all the new updates. This article will specifically talk about generative AI, the use of it, and how this system may impact future businesses and society as a whole. However, before getting into the ethics as well as the advantages and disadvantages of using generative AI, let’s first understand what generative AI actually means.
What Is Generative AI?
The concept of artificial intelligence isn’t anything new and can be originated back as early as 1956. Only in recent years, however, it is starting to take effect, with generative AI being the most current edition. This is a form of artificial intelligence that’s able to create a wide range of content, spanning from text and images to synthetic data and audio.
The term, generative, is used because it creates something entirely new. How generative AI works is achieved through machine learning. It takes a huge amount of data and processes that information to create algorithms that might match the prompt it was provided with.
Some examples of generative AI include:
- ChatGPT: It serves as a free chatbot that instantly produces a response to practically any and every question it’s asked.
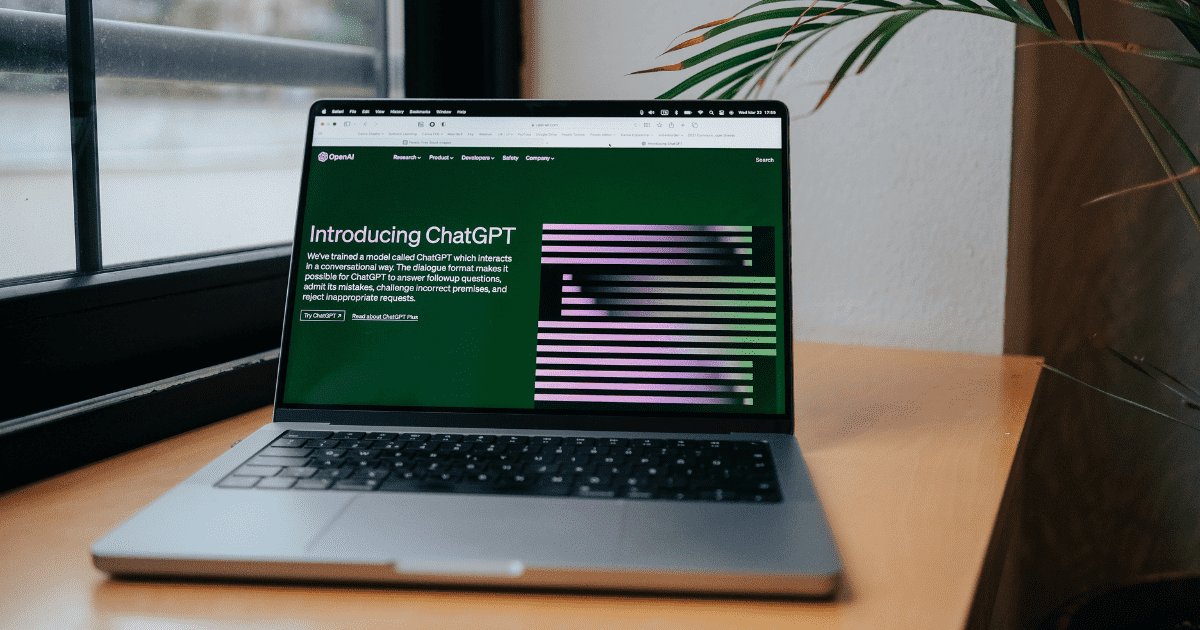
- DALL-E: A system that can create realistic images or art just from a simple description.
- Sharly.ai: A productivity tool that saves time by summarising long documents for an easier reading experience.

This is only the tip of the iceberg of what generative AI can do. As the mass population and professionals begin to experiment with and adopt this new technology, it will very likely continue to change the way jobs are being performed.
How Generative AI May Impact Jobs & Businesses
In recent years, we have seen many brands and companies from various industries putting this new technology to work in their fields. Here are some examples of how Generative AI is shaking things up:
Fashion
Just recently, Levi’s announced their plans to introduce AI-generated models in place of real human models. Through their partnership with Laland.ai (a service that’s well-known for its hyper-realistic AI models), the famous jeans brand claims that this could create a new opportunity to improve diversity and body inclusivity in the fashion industry.
Presently, most clothing can be viewed on one model. However, with generative AI, consumers might be able to see these pieces on a model that more accurately reflects their own body shape and skin tone.
Copywriting
From social media and blog posts to email marketing content, copywriting tools like ChatGPT, CopyAI, and Jasper, are on the rise for their ability to generate multiple formats of copy efficiently. The use of natural language processing (NLP) helps to optimise the copy in a way that can easily meet objectives like boosting traffic, increasing brand awareness, and improving conversion rates.
Graphic Design
Generative AI can not only assist in the production of art but also offers additional design ideas to choose from. The system can also recognise the specific graphics that companies best prefer and provide a customised design that closely fits the brand’s image.
Furthermore, it can better streamline certain processes, such as scaling, colour correction, and cropping, so that graphic designers can focus their energy on other more pressing areas of their work.
Customer Service
Chatbots or other similar generative AI systems can provide 24-hour customer service by instantly generating human-like responses to a large number of customer inquiries. From their data input, they could then identify if there’s a consistent pattern of customer behaviour, preferences, or trends, and tailor their recommendations or responses accordingly.
Benefits of Generative AI
There’s no denying that the use of generative AI presents some major benefits to businesses and the workplace. These include:
- Efficiency: Certain business processes, like customer service, data analysis, and basic content creation can be automated with generative AI. This may help companies save time and allow them to concentrate their resources on other crucial sections.
- Cost-Saving: Automating menial and repetitive tasks can simplify unnecessary work structures, thereby allowing businesses to reduce costs and improve their productivity.
- Personalisation: As generative AI is trained to learn from user data, it can produce personalised content that specifically caters to customers’ interests. Curating content that’s more closely aligned with what the customer wants may boost engagement and sales.
- Innovation: With the benefit of efficiency and automation, many existing business models will face disruption. This would in turn drive innovation of newer ideas or product designs that have yet to be explored in the market with traditional methods.
- Flexibility: Generative AI can create a wide range of content, which enables businesses to apply this system to multiple formats, especially in marketing and advertising.
- Data Augmentation: Can improve current datasets by generating synthetic data to enhance the performance of machine learning.
Risks of Generative AI
There’s always a flip side to every coin. While generative AI can prove to be an essential asset to businesses, several potential risks need to be considered.
- Accuracy and misinformation: The content produced by generative AI might present inaccurate information, as the system cannot differentiate between truth from falsehood. Spreading false information may affect a business’ reputation negatively.
- Bias: Machines can also have some prejudice and biases in the training data. This might lead to discriminatory and biased outcomes. For instance, this viral tweet demonstrated how ChatGPT has already displayed sexist and racist content through its prompts.
- Malicious content: As with everything, generative AI can also be used with malicious intent. The images of organisations may be at risk, as cyber-criminals can increase their phishing attempts to create false imitations through scams and deep fakes.
Ethics & Data Protection In AI
Besides the risks mentioned, there’s also the question of intellectual property (IP) theft. The conflict of copyright comes into play when there’s no clear distinction of ownership to the creative works generated by AI. Some would justify that because the output created didn’t result from human creativity, it shouldn’t be eligible for copyright protection.
While others may strongly argue otherwise, as they stem from the processes of complicated algorithms, programming, and human input. Regardless of where one stands on this debate, the issue still remains and the ambiguities surrounding it may lead to plagiarism allegations further down the line if they aren’t addressed. Before utilising any AI-generated works, companies need to orchestrate frequent IP clearance searches to prevent any clashes with any existing IP rights.
Another issue that has been highlighted is in the area of security and data protection breaches. There is bound to be some sensitive information about users and organisations contained within the copious amounts of data that AI is processing for machine learning. If there are no proper security regulations placed, this private data could be leaked or misused by unauthorised parties.
As such, businesses that plan on introducing AI into their work structure need to be aware of the risks and start planning how to alleviate these issues. This might involve implementing even stronger privacy and data security protocols, such as regular security audits, conversation encryptions, and stricter access controls.
Where To Start with Generative AI?
Generative AI is undeniably a significant component that will powerfully transform how we work and interact with the world around us. That said, there remain risks to manage and ethical decisions to make.
Companies should start addressing three points. Firstly, deliberately decide how they are going to start with Generative AI or not start, and communicate it to the organisation. Secondly, understand how their immediate and future business models can change, and intentively embark in experimentation. Thirdly, fully understand and address the risks they may face, including around intellectual property, data protection, and cybersecurity.
Vittorio Furlan is an ICDM Member, the founder and managing director of Foray Advisory. He has two decades of international experience in digital transformation, data and AI, and he supported the transformation business and government agencies as a consultant and a managing director.
Credits:
- Robot pointing on the wall by Tara Winstead on Pexels.
- Open laptop on desk by Hatice Baran on Pexels.
- Source from DALL-E website.
- Source from Sharly.ai website.
- Source from Laland.ai website.
- Source from Copy.ai website.
- Source from Intercom website.
- Default photo by Shantanu Kumar on Unsplash.

 5.0
5.0